Explaining MTHFR?
(Register for FREE to read all the blogs)
Indeed, MTHFR serves as both the name of a gene and the enzyme it encodes. The term “MTHFR” is used as an abbreviation for the full name of the gene: methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. This enzyme plays a crucial role in various biochemical processes in the body, particularly in the metabolism of folate (vitamin B9) and the conversion of homocysteine to methionine. The gene provides instructions for the synthesis of the MTHFR enzyme, and variations in this gene can impact the enzyme’s activity, potentially influencing health outcomes.
Welcome to MTHFR Experts. We are part of BodyScience.life a functional medicine clinic located in South Miami, FL.
This blog has information we’ve been collecting for the past 8 years as well as several Webinars by our Scientific Director, Amy Jaramillo
You can register right now for a FREE membership and immediately have access our educational articles and webinars.
If you would like a consultation with our medical team, please call 305.901.5888
Fertility and MTHFR
What is MTHFR?
The MTHFR enzyme facilitates the addition of a methyl group to folic acid, rendering it usable by the body. Produced by the MTHFR gene, this enzyme is essential for the effective utilization of vitamin B9. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in the conversion of homocysteine into methionine, vital for proper metabolism, muscle growth, and the creation of glutathione. Individuals with a mutation in the MTHFR gene may encounter challenges in efficiently eliminating toxins from the body.
The MTHFR gene provides instructions for the synthesis of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, an enzyme pivotal in processing amino acids, the fundamental constituents of proteins. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase plays a key role in a chemical reaction involving various forms of the vitamin folate, also known as vitamin B9. Specifically, it converts 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate into 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, a critical step in the multistep process transforming the amino acid homocysteine into methionine. Methionine is utilized by the body for the synthesis of proteins and other essential compounds.
What Are The Possible MTHFR Mutations?
There are TWO MTHFR genes, the MTHFR-C gene and the MTHFR-A gene and you have two copies of each of these (one from your mother and one from your father). This means there is a whole variety of ways that things could go wrong… Let’s look at those here:
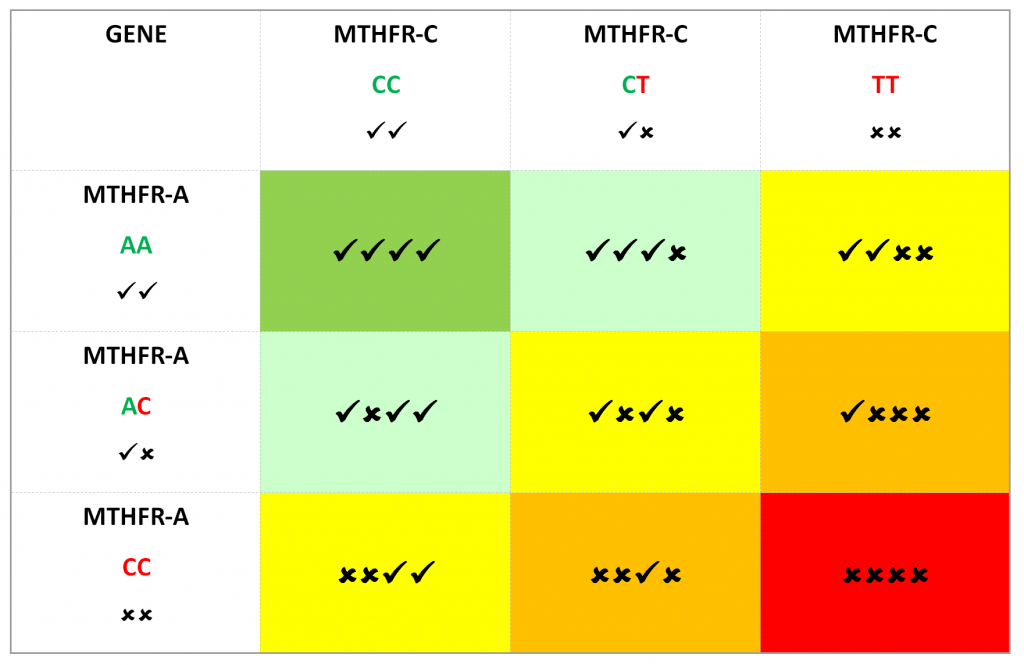
Remember that the mutation can be re-written with both letters at the end (for example C677T = 677CT) or even just the letters with no numbers (for example CT or TT):
- MTHFR C677C = normal MTHFR gene
- MTHFR C677T = heterozygous mutation (one mutation)
- MTHFR T677T = homozygous mutation (two mutations)
- MTHFR A1298A = normal MTHFR gene
- MTHFR A1298C = heterozygous mutation (one mutation)
- MTHFR C1298C = homozygous mutation (two mutations)
- MTHFR C677T + MTHFR A1298C = a compound heterozygous mutation
The MTHFR nucleotide at position 677 in the gene has two possibilities: C (cytosine) or T (thymine). C at position 677 (leading to an alanine at amino acid 222) is the normal allele. The 677T allele (leading to a valine substitution at amino acid 222) encodes a thermolabile enzyme with reduced activity.
Individuals with two copies of 677C (677CC) have the most common genotype. 677TT individuals (homozygous) have lower MTHFR activity than CC or CT (heterozygous) individuals. About ten percent of the North American population are T-homozygous for this polymorphism.
What Is Heterozygous and Homozygous MTHFR?
MTHFR mutations are typically referred to as heterozygous or homozygous.
The prefix “hetero” means different.
The prefix “homo” means same. Zygous just refers to degree of similarity.
In genetics, hetero- and homo- refers to the two alleles on the gene. For example, for C677T the alleles are C and T, which are different and therefore heterozygous.
Heterozygous
Heterozygous MTFHR means you have one copy of the mutant allele on the MTHFR gene.
Homozygous
Homozygous MTHFR mean you have two copies of the same mutant allele, which is considered more severe. It looks like this T677T, although it is typically just referred to as homozygous C677T.
So homozygous C677T actually means T677T.
Compound Heterozygous
There is also compound heterozygous, which is when you have one mutant allele on both the 677 and 1298 base position.
Reaction and metabolism
The overall reaction catalyzed by MTHFR is illustrated below. The reaction uses an NAD(P)H hydride donor and an FAD cofactor. The E. coli enzyme has a strong preference for the NADH donor, whereas the mammalian enzyme is specific to NADPH.
Problems From an MTHFR Gene Mutation
Individuals with reduced MTHFR enzyme activity may exhibit heightened homocysteine levels, a condition linked to inflammation and cardiovascular diseases, birth defects, challenging pregnancies, and a potential compromise in detoxification capabilities.
Deficiencies in folate, B6, and B12 nutrients have been correlated with elevated homocysteine levels.
Those with the MTHFR gene face challenges in processing folic acid, commonly found in inexpensive supplements and added to processed foods. Some experts suggest that this form of folic acid may accumulate in the body, leading to toxicity. Research has indicated an increased risk of cancer associated with folic acid supplements, providing yet another reason to steer clear of processed foods and reconsider multivitamin consumption.
Types of MTHFR Mutation
The realm of MTHFR gene mutations encompasses numerous possibilities, and ongoing scientific research aims to comprehensively grasp their intricacies. Below are links to more detailed resources, but a few common mutations exist.
The diversity in mutations arises from variations in the specific genes inherited from each parent. Simply put, if both parents transmit healthy genes, an individual won’t have a mutation. When one parent passes on a healthy gene and the other transmits a mutated one, several variations can manifest. If both parents pass on a mutated form, numerous scenarios may unfold.
The most consequential mutations, denoted by the locations C677T and A1298C on the gene, present distinct challenges. The prevalent forms of MTHFR mutation involve diverse combinations of these genes passed down from each parent:
- Homozygous: When the same gene is inherited from both parents, whether it be the 677 mutation or the 1298 mutation.
- Heterozygous: When one parent transmits the 677 mutation or the 1298 mutation, while the other transmits a normal gene.
- Compound Heterozygous: When one parent transmits the 677 mutation, and the other transmits the 1298 mutation.
Additionally, there are more advanced and rare mutations that contribute to the complexity of MTHFR gene variations.
What Happens When the MTHFR Gene is Defective?
Those with a defective MTHFR gene have an impaired ability to produce the MTHFR enzyme (estimates range from 20%-70% or more). This can make it more difficult to break down and eliminate not only synthetic folic acid but other substances like heavy metals.
Since folic acid can’t be converted into the usable form, it can build up in the body, which can raise levels of homocysteine. High homocysteine levels are associated with a higher risk in cardiovascular disease. This also affects the conversion to glutathione, which the body needs to remove waste and which is a potent antioxidant.
In short, we are just learning the extent to which this can affect health, but there is strong evidence that because of the affect on methylation, it can increase cancer risk, cardiovascular disease risk, risk of fetal development problems and more. It can also possibly contribute to or exacerbate other problems like autoimmune disease, mental issues and more.
Can I Fix a MTHFR Gene Mutation?
You are born with a fixed set of genes, and this genetic makeup remains constant throughout your life—immutable. While this might seem discouraging, the positive aspect is that there are ways to navigate around sluggish enzyme pathways. This can be achieved by supplementing with methylated forms of B vitamins, ensuring that the genetic inability to convert them does not impede their effectiveness. Additionally, incorporating methyl donors into your regimen can prove beneficial. While an MTHFR mutation may pose challenges, understanding and addressing it appropriately can transform it from a potential source of distress to an obstacle that can be overcome.
Biome IQ is the only company with a certified line of medical grade supplements designed for MTHFR mutations. Our products exceed the general professional guidelines, offer maximum purity, exceptional absorbability and have been clinically proven.
MTHFR Tips
Although it’s impossible to alter one’s genes, there are proactive measures that can be taken to minimize potential issues or prevent problems in children, particularly before and during the mother’s pregnancy. Some beneficial practices include:
Prioritizing Gut Health: Given the compromised ability to utilize certain nutrients, maintaining optimal gut health becomes crucial. This involves avoiding antibacterial soaps, vegetable oils, processed grains, and refined sugars. Instead, focus on fermented foods and homemade broth to enhance nutrient absorption. This approach also helps prevent candida overgrowth, which can exacerbate MTHFR-related issues.
Limiting Exposure to Environmental Toxins: Individuals with an MTHFR gene defect face challenges in eliminating toxins. Minimize exposure to plastics, chemicals in beauty and cleaning products, and scented candles, as they can release harmful substances. Employ houseplants and other methods to purify indoor air, and use water filters for drinking and shower water.
Avoiding Folic Acid: Refrain from consuming anything containing synthetic folic acid, as it is ineffective for those with an MTHFR defect and can be toxic. Instead, opt for supplements with L-MTHF forms, the methylated forms the body can utilize. Consider products like Biome IQ – PURE METHYLATION, a super B-complex designed for individuals with methylation deficiencies.
Incorporating Leafy Greens: Dark leafy greens provide the methylated forms of folate necessary for individuals with a gene defect.
Steering Clear of Processed Foods: Many processed foods contain synthetic folic acid, making it another reason to avoid such products.
Being Mindful of Medications: Certain medications, including hormonal contraceptives, can interfere with folate levels. Additionally, antacids may hinder B-12 absorption.
Avoiding Heavy Metals: Be cautious about heavy metals in both diet and the environment, as they are more challenging to eliminate for those with a gene defect.
Supporting Detoxification: Since individuals with an MTHFR defect have a compromised ability to eliminate toxins, supporting the body’s natural detoxification pathway is crucial. Consider supplements like BiomeIQ – MTHFR DETOX to aid in this process.